What we cover in this blog
Key Takeaways
- User-centric design and iterative processes drive seamless digital experiences.
- An iterative UX design process ensures continuous improvement and user satisfaction.
- Advanced prototyping tools refine designs before implementation.
- Usability testing identifies and addresses issues for a seamless experience.
- Continuous improvement through analytics optimizes digital experiences.
The UX Design Process
UX design is a crucial, iterative design process that enables businesses and brands to create digital products that are user-friendly, efficient, and enjoyable to use. By creating digital products and employing the right UX design principles, designers can ensure that the end-users have a positive experience while using the product.
The key to successful UX design is understanding the users and their needs. Designers perform thorough research and analysis to gain insights into user preferences and behaviors, which establish the design process. They craft user personas, user journeys, diagrams, and wireframes to visualize and structure user interactions. These tools provided by the application development software company help designers create a product that meets users’ needs and expectations while delivering a seamless and enjoyable experience.
a. Research phase
User research is conducted through user interviews, surveys, and questionaries, creating focus groups, referring to various ethnographic studies, and comparing data analytics of competitor and market data. Finally, stakeholder interviews will be conducted to collect valuable insights on user satisfaction.
b. Design phase
The design face involves routing proper sitemaps and creating a proper navigation process with an expert content strategy to elevate the user-centric design wireframes and visual elements. Further, the prototyping, branding, UI design, and establish the design of the UX model.
c. Testing phase
After the design phase, the next milestone diverse users need to achieve is to pass through various stages of testing, such as accessibility, usability, and performance testing, before approving the design.
d. Implementation phase
The implementation phase involves the handover of the product from the design to the software development team, which further gets filtered by front-end and back-end development and quality assurance. Then, the final product is deployed to the intended user sector.
e. Evaluation phase
The evaluation phase collects analytics and performance metrics from user feedback and iterates and checks for areas of improvement to meet the user satisfaction expectations further.
UX design aims to create an enjoyable user experience. Keep the user’s needs in mind, collect feedback, and refine your design until it aligns with their requirements. Follow each step of the process, iterate, and test continuously. Take a measured approach, explore diverse design concepts, and find what resonates best with your users.
Prototyping
A prototype is an early model of a product design or system that can be incredibly beneficial for UX/UI designers. It provides a platform for designers to evaluate, test, and refine their designs, which is an essential part of the UI UX Design process that usually comes after ideation.
Prototyping is an iterative process of quickly building a simplified model version of a product or system to test ideas, gather feedback, and refine the final solution. By prototyping before the development of the product, designers can obtain clear solutions to improve it and to establish that the user needs are met.
Prototypes are extremely important during the design process as they allow designers to test and revise a design before it becomes final. Prototypes not only save time but also help designers create a product that meets the expectations of the users.
Outlined below are the steps for creating the prototype
- Analyzing the requirement
- Designing and creating the prototype
- Testing and refinement of prototype
- Preserving the design process
- Launching the test results and implementing the product
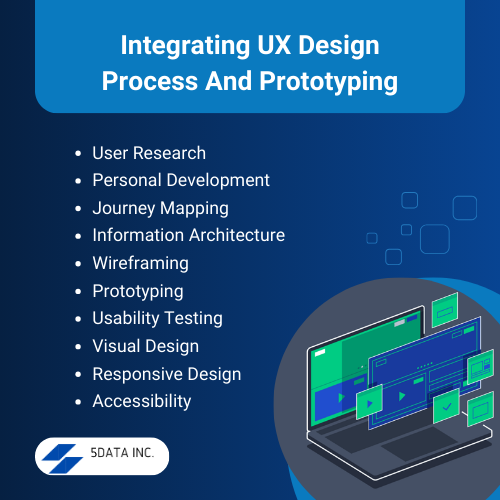
Integrating UX Design Process And Prototyping
Crafting seamless digital experiences is a user-centric process that involves a blend of user research, intuitive design, and advanced prototyping techniques. Start with a comprehensive understanding of user personas and journey mapping to deeply understand user expectations and needs. Utilize advanced UX design tools like Figma or Adobe XD for prototyping, ensuring interactions are smooth and intuitive. Continuously improve based on user feedback to refine the experience further, making the audience feel valued and integral to the design process.
Crafting seamless digital experience strategies for advanced UX design and prototyping under the assistance of a software application development company involves several key steps:
1. User Research
Understand your target audience through in-depth research, including interviews, surveys, user testing, and usability testing. Gain insights into users’ interactions, their preferences, needs, and pain points.
2. Persona Development
Create a detailed user report based on your research findings. These personas represent your target audience segments and help guide design decisions for voice user interface.
3. Journey Mapping
Tracking the journey from initial interaction with the user to conversion and beyond. Identify touchpoints and opportunities for improving the user engagement experience.
4. Information Architecture
Develop a clear and intuitive information architecture for your digital product. Organize content and navigation in a way that intuitive navigation makes sense to users.
5. Wireframing
Create low-fidelity wireframes to outline the layout, user interfaces, interactive features, and structure of your digital product. Focus on user flow and functionality rather than visual design at this stage.
6. Prototyping
Use advanced prototyping tools like Figma, Adobe XD, or Sketch to create interactive prototypes. These prototypes should simulate the user experience and allow for user testing and feedback.
7. Usability Testing
Usability testing plays a crucial role in crafting seamless digital experiences. Conducting usability testing with real users identifies any usability issues or pain points. Improve your designs based on the feedback received, instilling confidence in the audience about seamless user experience, interface, and the effectiveness of the design.
8. Visual Design
Once the interaction design for crafting digital experiences is solidified, incorporate visual design elements to enhance the aesthetic appeal and branding of your next digital platform or product.
9. Responsive Design
Ensure that your digital user experience is optimized and responsive for various devices and screen sizes. Test digital design across different devices to ensure consistency.
10. Accessibility
Design your web and mobile applications with accessibility in mind to increase user engagement, including those with disabilities who can access and use your digital product effectively. Taking the assistance of an expert mobile application development company makes the above functionality successful.
By following these steps and prioritizing user needs over business objectives throughout the design process, you can craft seamless digital experiences that delight users and drive user engagement.
Conclusion
Continuous improvement is a key pillar to business success in crafting seamless digital experiences. Implementing analytics tools to record user behavior and gather insights for ongoing optimization. Regularly update and refine your digital experience based on user feedback and data analysis, inspiring the audience for ongoing optimization.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do you approach designing a seamless and beautiful user experience?
By integrating various techniques, design, and development processes and leveraging prototyping to enhance the results, one can achieve a seamless and beautiful user experience.
2. What is the role of user research in UX Design?
User research is a vital tool for creating successful designs. By combining different methods such as surveys, interviews, and analytics, valuable insights can be gained into the users’ needs and preferences. This information can be used to create design solutions that are user-centered, intuitive, and effective.
When designing a user experience, it is crucial to establish a solid foundation that is centered around clear objectives. The project’s goal should be specific, measurable, and aligned with the user’s requirements. It’s essential to outline the primary project objectives, encompassing budget, schedule, and criteria for assessing the overall effectiveness of the application or website. By defining the project’s objective, users can easily find the information they need, leading to a more positive user experience.
3. What are the five processes of UX design?
The five important stages of the UX design process are listed below:
- Research phase
- Design phase
- Testing phase
- Implementation phase
- Evaluation phase
4. What growing trends should UX designers keep in mind when designing any user experiences?
The following trends dictate the future of the UX designing and development process.
- 3D and 3D abstractions and animations
- Neumorphism and glass morphism
- 2D illustrations
- Low poly illustrations
- Clean and simple designs in complex interfaces
- Monochromes
- Text trends, etc.