What we cover in this blog
What is Data Lifecycle Management?
Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) is a system for managing data throughout its lifecycle from the point of data initialization to the point of data deletion. Data is divided into phases based on various criteria, and as it completes various tasks or satisfies particular requirements, it advances through these stages. A good DLM process gives a business’s data structure and organization, enabling important process goals like data availability and security.
These objectives are essential to deliver the best results and become more significant over time. Businesses can prepare for the severe implications of data breaches, data destruction, or system failure, thanks to DLM policies and procedures. Data protection and disaster recovery should be prioritized in a DLM strategy, particularly given the invasion of spammers into the digital environment brought on by the rapid growth of data. It will prevent devastating effects on a brand’s bottom line and overall reputation by having an effective data recovery plan in the event of a disaster.
Information Lifecycle Management (ILM) VS. Data Lifecycle Management(DLM)
Many people get confused between both terms, and they believe it’s the same. But it’s not as we think! Although both components are used for a data management plan, Information Lifecycle Management (ILM) and Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) are different.
File-level data is managed by DLM, which organizes files according to their type, size, and date. ILM, on the other hand, takes care of managing the various data elements within a file, ensuring data accuracy and regular updates. User data like email addresses or account balances are included in this type.
The Five Stages of Data Lifecycle Management
By understanding the five stages of the data lifecycle mentioned below, organizations can develop a plan to manage data throughout its entire lifecycle, from creation to archiving or deletion. These can help ensure the data is accurate, complete, and available when needed while eliminating permanent data loss and ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Data collection: This is the stage where data is initially created, such as through data entry, data acquisition, or data generation. It is the initial stage of the data’s lifecycle.
- Data processing: Once data is created, it goes through a processing stage, where it is structured, visualized, and analyzed. This stage is important for ensuring the data is accurate, complete, and in the correct format.
- Data distribution: After data has been processed, it is distributed to different systems, applications, and users for further use while maintaining data integrity. This stage ensures that the stored data is available to those who require it.
- Data archiving and retention: As data ages, it may no longer be needed for active use and should be moved to an archive or retention system. This stage involves classifying data, setting retention periods, and determining how data should be disposed of.
- Data disposition: This is the final stage of the DLM process, where data no longer needed is taken care of, either by deletion or permanent archiving. This stage ensures that data is disposed of securely and promptly.
Benefits Of Data Lifecycle Management
Data lifecycle management is beneficial for any company that stores and uses internal and external data, though it is more applicable to some organizations than others. If the data management plans are not clearly defined, your company will inevitably lose or be unable to find a crucial file or byte of data. However, by implementing the proper data regulations, your company can reduce the risk of data loss, deletion, breaches, and associated fines and penalties.
So, how do we achieve the ideal data lifecycle management process?! The answer lies in the pie! We will cover the five best practices for data lifecycle management here.
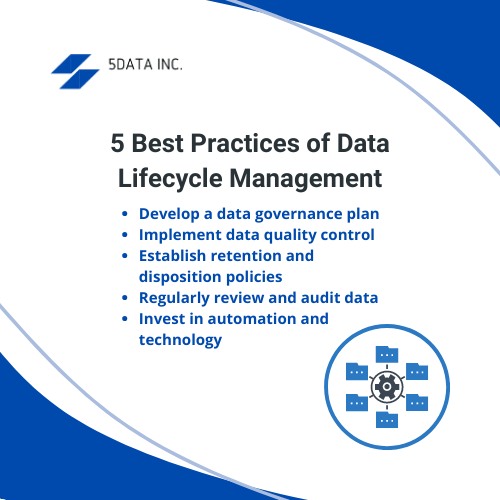
5 Best Practices of Data Lifecycle Management
According to a study by Harvard Business Review Analytics Services, fewer than 26.5 percent of businesses claim to have a data-driven organization. These indicate that companies should adopt a strategy ensuring their data is completely governed, discoverable, trusted, and well-connected. The five best practices of DLM include the following:
- Develop a data governance plan: A plan to manage data is essential for maintaining its integrity and accuracy. This plan should include guidelines for collecting data, managing existing data, and storing data. For example, A financial services company may outsource a team of data management experts to collect sensitive financial data in an encrypted format.
- Implement data quality control: Ensuring the quality of your data is a crucial aspect of DLM. Implementing data quality control measures, such as data validation, managing active data, and standardization can ensure that your data is accurate, complete, and free from unstructured data. For instance, A healthcare organization may use software to automatically check for errors in patient information, such as misspelled names or incorrect birthdates, and correct them before the data is stored.
- Establish retention and disposition policies: Establishing retention and disposition policies is essential for managing the lifecycle of your data. These policies should include guidelines for how long data should be retained and when it should be deleted or archived. For example, A retail company may establish retention and disposition policies for their customer data, such as retaining customer data for seven years after their last purchase and disposing of any data that is no longer needed. They may also have a policy in place for securely disposing of sensitive data, such as credit card information, by industry regulations.
- Regularly review and audit data: Regularly reviewing and auditing data is important for identifying and correcting any issues. It includes checking for errors, inconsistencies, and duplicate data. A logistics company may regularly review and audit enterprise data, such as tracking data for their delivery trucks, to identify and correct any issues. They may use data analytics software to analyze the data, detect anomalies or inconsistencies and make necessary corrections.
- Invest in automation and technology: Automating DLM processes can save time and resources while ensuring that data is managed consistently. Investing in technology, such as data management software and archiving solutions, can help automate DLM processes and improve data management efficiency. Likewise, A manufacturing company may invest in automation and technology to manage their DLM processes, such as using data management software to automate archiving and deleting inactive data. These can help them achieve data maintenance efficiently for the entire organization and ensure compliance with regulations.
Your Best Data Management Service Provider
Choosing a DLM service provider can be a game-changer for your business. With the help of a data life cycle management service provider, you can focus on your core business dynamics while experts handle your entire organization’s data.
5Data Inc is the leading provider of data lifecycle management services. They utilize advanced technologies such as predictive analytics and machine learning to extract valuable insights from data. Their scientific approach and expertise in data management plans include creating data, storing data, removing data redundancy, data archival, data backup, managing different data types, and delivering data.
These will help your business make better decisions and optimize your data capture strategy. Don’t hesitate to contact 5Data Inc today and take your business to the next level.