Data migration is the process of transferring data from one system to another. Data is extracted from the source system, transformed to fit the target system’s structure, and then loaded into the target system. During the migration data cleansing process, to ensure data integrity, security, and quality are ensured. Depending on the organization’s needs, data migration can be a one-time process or an ongoing activity.
What we cover in this blog
- Key Takeaways
- Essential Insights for Successful Data Migration
- Types of Data Migration
- The Roadmap to Successful Data Migration
- The Data Migration Process : Tools and Technologies
- Overcoming Challenges and Ensuring Success
- Evaluating Success and Maintaining Compliance in Data Migration
- Post-Migration Activities in Data Migration
Key Takeaways
- Effective data migration requires thorough planning, including assessing current systems, addressing data quality issues, and defining clear project milestones.
- Utilize ETL tools and automation to streamline data mapping, transformation, and testing while ensuring data integrity and security throughout the migration process.
- Migrate in stages, validate each phase, and implement robust data governance policies to maintain compliance and protect sensitive information.
Essential Insights for Successful Data Migration
Data migration is the critical process of transferring information from one system to another, enabling organizations to update technology, consolidate data storage, or transition to more efficient platforms. A seamless migration involves several vital steps, including assessing existing data, devising a robust strategy, cleaning and validating data, executing the transfer, and ensuring the new system operates smoothly. When executed correctly, data migration enhances data accessibility, boosts system performance, and aligns with organizational goals, driving efficiency and growth.
Types of Data Migration
The data migration can be classified as below:
- Database migration: transferring data from one database management system to another.
- Application migration: moving a software application from one computing environment to another.
- Business process migration: transferring databases and applications containing data related to customers, products, and operations.
- Cloud migration: moving data, applications, or other business elements to a cloud environment.
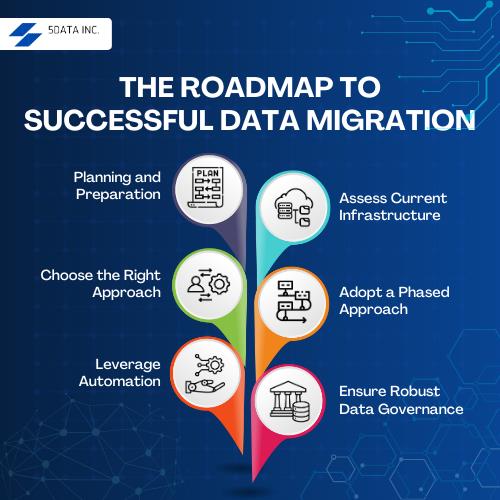
The Roadmap to Successful Data Migration
1. Planning and Preparation
Assess the systems and data’s current state and identify any data quality issues. Define the target database and state, including the new data structure, format, and relationships between key components. Construct a detailed project plan that outlines timelines, identifies the resources needed, and highlights key milestones for successful execution. Identify potential risks and the necessary tools and technologies for the migration process.
2. Assess Current Infrastructure
Perform a thorough inventory of existing systems, applications, and data. Identify dependencies, data silos, and legacy systems that may hinder migration. Evaluate data quality and address issues such as duplicates, errors, or incomplete records.
3. Choose the Right Approach
Move existing data and applications directly to the new platform with minimal changes. Migrate while making small optimizations to leverage new environment features. Completely redesign systems for full modernization.
4. Adopt a Phased Approach
Migrate in stages, focusing on non-critical data or systems first. To reduce risk, validate each phase before proceeding. Use pilot projects to test workflows and identify potential bottlenecks.
5. Leverage Automation
Utilize automated tools for data mapping, transformation, and migration. Automate testing to ensure data integrity, enhanced security, and functionality after the migration strategy.
6. Ensure Robust Data Governance
Define clear policies for data ownership, security, and compliance to protect sensitive information, including encryption, access controls, and regular audits.
The Data Migration Process : Tools and Technologies
ETL tools play a crucial role in streamlining the processes of extracting, transforming, and loading data storage systems from cloud providers, thereby enhancing overall efficiency. Data migration software is specifically tailored to facilitate the seamless transfer of data. It often comes equipped with valuable features such as data mapping, validation, and reconciliation, which ensure accuracy and reliability. Additionally, cloud migration tools provided by the best application development services offer organizations effective solutions for transitioning their data and applications to the cloud, supporting their technological advancement and flexibility.
Overcoming Challenges and Ensuring Success
Common challenges in data migration and Solutions:
- Data loss or corruption: ensuring that all data is accurately transferred from the old system to the new one.
- Data consistency: maintaining consistency of data across different systems.
- Data mapping: Mapping data from the old system to the new one can be time-consuming and error-prone.
- Data validation: Enhancing the accuracy and completeness of the migrated data to ensure a successful transition.
- Data security: Implementing effective measures to protect sensitive data throughout the migration process.
Evaluating Success and Maintaining Compliance in Data Migration
a. Measuring the Success
Tracking the success of key phases of the data migration by hitting benchmarks. Validating that everything was completed successfully. To enhance our understanding of the migration process, we will be receiving validation reports that provide a detailed comparison of the migration logic with the original and current states of objects, data, and users. Migration will allow us to assess the effectiveness of critical components of the migration and address any discrepancies. Data collection and data management service providers guide businesses in organizing data structures.
b. Engage Stakeholders
Collaborate with critical stakeholders, IT teams, and end-users to ensure alignment and buy-in. Provide training to familiarize staff with new systems and processes.
c. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
To meet industry standards and regulations, such as HIPAA and GDPR, we can prioritize the implementation project management of robust data security measures, including access controls and data encryption. Additionally, robust testing, conducting regular audits, and assessing risks is useful in identifying areas for improvement and attaining sustained compliance over time.
Post-Migration Activities in Data Migration
a. Post-Migration Testing and Validation
Test the migrated data to ensure it is accurate and complete, validate that the data is properly formatted and that consistent data formats can be accessed by authorized users, and conduct user acceptance testing to ensure the migrated data meets business requirements.
b. Plan for system downtime and recovery
Schedule migration during low-impact periods to minimize disruption. Create a contingency plan and backup data to mitigate the impact of unexpected failures.
c. Continuous Monitoring and Optimization
Regularly assessing the migrated data to ensure its completeness and accuracy. Enhancing the data migration process to boost efficiency system performance and lower costs. Proactively identifying opportunities for improvement and implementing thoughtful changes to foster long-term success in storage migration. Data life cycle management services provide the necessary insights to navigate these data processes.
Conclusion
Data migration is key for modernizing organizations. It helps them improve efficiency, cut costs, and make better decisions. To ensure a successful data migration project, focus on careful planning, executing the plan well, and monitoring progress over time. By emphasizing these elements, organizations can meet their goals and make the most of their data migration strategy. Using best practices and the right software tools will lead to successful data migration and help achieve modernization goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the 6 R’s of migration strategy?
Determining the best path for cloud migration can be overwhelming due to the many options available. This guide outlines the 6Rs framework: rehosting, re-platforming, repurchasing, refactoring/re-architecting, retiring, and retaining on-premise resources.
2. What are the key considerations for data migration?
- Compliance: Ensure alignment with industry-specific regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA.
- Scalability: Design systems to accommodate future growth.
- Cost Management: Balance the benefits of modernization with budgetary constraints.